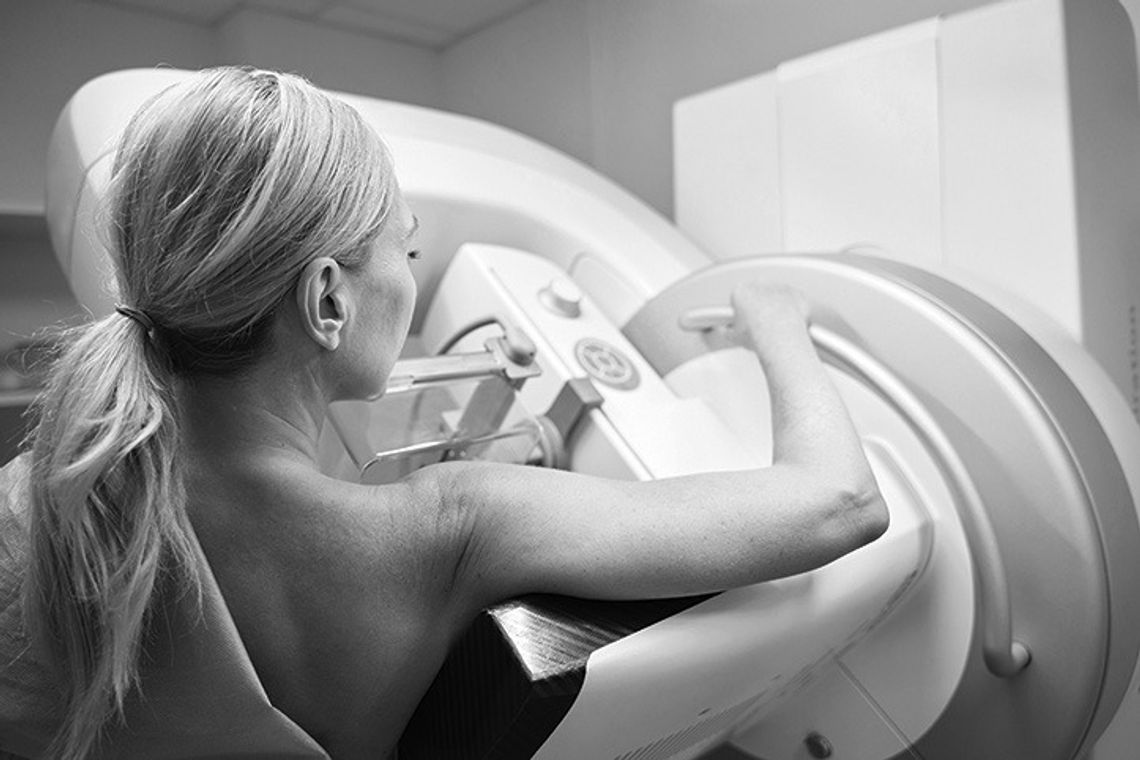
Mammograms remain the most effective method for diagnosing breast cancer and catching the disease in its earliest, most treatable stages. While various health organizations recommend different screening intervals, the American Cancer Society advises annual mammograms for women ages 40 to 54. Women age 55 and older who adhere to ACS recommendations can switch to a mammogram every two years if in good health.
Mammograms employ low-dose X-rays to map out breasts and detect unusual growths. There are two main types of mammogram: screening and diagnostic.
SCREENING MAMMOGRAM
The Breast Cancer Research Foundation says a screening mammogram detects changes in breast tissue that could be indicative of breast cancer in women who exhibit no other symptoms of the disease. Mammograms sometimes can detect breast cancer up to three years before a person or doctors feel a lump. During the test, the breasts are flattened between two imaging plates from a few angles to get the X-rays.
DIAGNOSTIC MAMMOGRAM
Should a screening mammogram show something amiss or not easily visible the first time around, radiologists may ask the person to come back for additional image testing. This diagnostic mammogram includes additional views. The National Breast Cancer Foundation says diagnostic mammograms take detailed X-rays of the breast using specialized techniques. They also may involve additional views or adjunct testing like ultrasound or MRI to provide a better overall picture of breast health. Diagnostic mammograms may be used to zero in on a specific area of the breast that needs further clarification.
Because a diagnostic mammogram requires taking a greater number of images, it will expose a patient to a higher dose of radiation. Still, health professionals feel the risk is worth it to help rule out cancer. Also, unlike a screening mammogram that may take several days for a radiologist to read and identify results, a diagnostic mammogram can reveal important information immediately.
Screening and diagnostic mammograms are important tools used to check for breast cancer.